Two of the most common types of welding are arc welding and MIG welding. Both methods are widely used in various industries, and it is essential to understand their differences and similarities to determine which method is best for a particular application.
Arc Welding
Arc welding is a highly effective fusion welding process commonly used for joining metals. During this process, an electric arc generated from either an AC or DC power supply produces an intense heat of approximately 6500°F, causing the metal to melt at the joint between two workpieces. The arc can be either manually or mechanically guided along the line of the join, while the electrode either simply carries the current or conducts the current and melts into the weld pool simultaneously to supply filler metal to the joint.
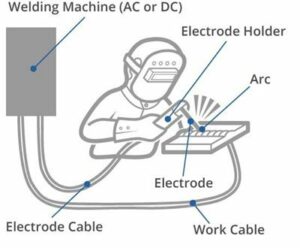
One of the challenges in arc welding is the chemical reaction of metals to oxygen and nitrogen in the air when heated to high temperatures by the arc. To overcome this, a protective shielding gas is used to minimize the contact of the molten metal with the air. This not only protects the weld pool but also helps in achieving a smooth finish. Once the molten metals are cooled, they solidify to form a metallurgical bond, which results in a strong and durable joint.
Technical Setup and Specifications for Arc Welding
Arc welding requires a power source, electrode holder, ground clamp, and welding cables. The power source is responsible for producing the electrical arc, and it can be either an AC or DC source. The electrode holder holds the electrode, and the ground clamp is attached to the workpiece to complete the electrical circuit. Welding cables connect the power source, electrode holder, and ground clamp.
Types of Arc Welding
There are several types of arc welding, including shielded metal arc welding (SMAW), gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW), and flux-cored arc welding (FCAW). SMAW, also known as stick welding, is the most commonly used type of arc welding. GTAW, also known as TIG welding, is used for the precise welding of thin materials. FCAW, on the other hand, is used for welding thick materials and is often used in construction and heavy equipment repair.
We have great articles on all types of arc welding techniques, so be sure to check them out before continuing with this one.
Strengths and Weaknesses of Arc Welding
One of the main strengths of arc welding is its versatility. It can be used to weld various materials, including carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and cast iron. Plus, it’s relatively inexpensive compared to other welding methods.
However, arc welding has some limitations, such as the need for a clean and dry work area and the difficulty of welding thin materials. It produces a significant amount of spatter and requires a high level of skill to achieve high-quality welds.
Best Applications for Arc Welding
Arc welding is commonly used in various industries, including construction, automotive, and manufacturing. It is best suited for welding thick materials and for applications where a high degree of strength is required. It is also ideal for outdoor welding applications, as it can be used in windy conditions with the appropriate equipment.
MIG Welding
MIG welding, also known as Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW), is an advanced arc welding process that utilizes a continuous solid wire electrode, fed through a welding gun, to join two base materials together. A shielding gas, typically a mixture of argon and carbon dioxide, is also sent through the welding gun to protect the weld pool from contamination. The name MIG, which stands for metal inert gas, reflects the use of inert gas, such as argon, as a shielding gas.
One of the main advantages of MIG welding is its versatility, enabling artists, farmers/ranchers, motorsports enthusiasts, or DIY welders to make most types of fabrication and maintenance/repair welds on materials ranging from 24-gauge to 1/2-inch thick. Additionally, MIG welding is preferred by many due to its relative ease of use. With proper guidance and practice, most people can become competent MIG welders.
Despite its simplicity, MIG welding requires careful attention to welding parameters, including voltage, current, wire speed, and gas flow. These settings may vary depending on the materials being welded, the wire diameter, and the joint configuration. Understanding these technical specifications is crucial in producing high-quality welds that meet the requirements of the project.
Technical Setup
MIG welding requires a power source, wire feeder, welding gun, shielding gas, and welding cables. The power source provides the electrical current, and the wire feeder delivers the electrode wire to the weld area. The welding gun is used to control the wire feed and the shielding gas flow. The shielding gas is typically a mixture of argon, carbon dioxide, and helium.
Types of MIG Welding
Several types of MIG welding include short-circuiting transfer, spray transfer, and pulsed spray transfer. The short-circuiting transfer is used for welding thin materials, while spray transfer is used for thicker materials. Pulse spray transfer is used for the precise welding of thin materials and is often used in the aerospace and automotive industries.
Strengths and Weaknesses of MIG Welding
One of the main strengths of MIG welding is its ease of use. It is a simple process that produces high-quality welds with minimal spatter. It is also faster than arc welding and can be used to weld a variety of materials, including aluminum, stainless steel, and mild steel. However, it is more expensive than arc welding, and it requires a clean work area and a constant supply of shielding gas.

Best Applications for MIG Welding
MIG welding is a widely used welding method in the automotive, manufacturing, and construction industries. It is ideal for welding thin to medium-thick materials and is preferred for applications that require speed and efficiency. It is especially effective for welding non-ferrous metals like aluminum and copper. It’s a versatile and efficient process that produces high-quality welds with minimal spatter. Its relative ease of use makes it a popular method for welders of all skill levels.
Arc Welding vs. MIG Welding: Differences and Similarities
Arc welding and MIG welding are both popular welding methods, but they have several differences and similarities.
Differences
Similarities
Choosing the Right Method
When it comes to choosing between arc welding and MIG welding, it depends on what you’re working with and what you need to accomplish. If you’re dealing with thick materials that require a lot of strength, then arc welding might be the way to go. But if you’re working with thin materials that need to be precisely welded, then MIG welding might be a better choice. And if you’re in a hurry and need to get things done quickly, then MIG welding might be the most efficient option.

It’s important to remember that both methods have advantages and disadvantages. Arc welding is versatile and can be used for a variety of materials, but it can produce more spatter and be slower than MIG welding. Meanwhile, MIG welding is faster and easier to use, but it can be more expensive and requires a clean work area and a constant supply of shielding gas.
Ultimately, the decision to use arc welding or MIG welding will depend on the specific needs of your project. Just make sure you take the time to understand each method’s technical setup and specifications before making your choice. And remember to always take proper safety precautions and wear protective gear when welding.
Wrapping it up
In conclusion, arc welding and MIG welding are both popular welding methods that offer their own set of advantages and disadvantages. Arc welding is a versatile method that can be used for welding thick materials, but it produces more spatter and is slower than MIG welding. MIG welding, on the other hand, is a faster and more efficient method that is ideal for welding thin materials and is easier to use than arc welding.
When deciding between arc welding and MIG welding, it is important to consider the specific application and the materials being welded. Both methods require proper safety precautions and a clean work area. They also require a power source and welding cables but differ in the types of electrodes used and the need for shielding gas.
Ultimately, the decision to use arc welding or MIG welding will depend on the project’s individual needs. Understanding the technical setup and specifications of each method can help welders make an informed decision when it comes to selecting the right welding method for their project. Ultimately, the right welding method will produce high-quality welds that meet the requirements of the project while also being safe and efficient.







